The Periodic Table: A Comprehensive Guide to Full Names and Symbols of Elements
Welcome to this comprehensive guide to the Periodic Table! Whether you're a student, a science enthusiast, or just someone curious about the building blocks of our universe, understanding the Periodic Table is essential.
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
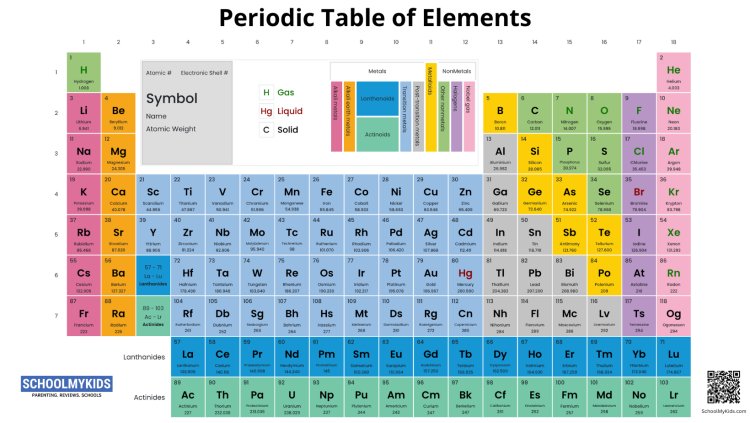
In this blog, we'll explore the full names and symbols of elements, making it easier for you to learn and remember. Before we begin, if you're looking for more educational resources and support for your studies, be sure to check out SchoolMyKids, an excellent online platform offering valuable resources to enhance your learning experience. Let's dive in!
The Periodic Table and Its Importance: The Periodic Table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. Dmitri Mendeleev is credited with the development of the first widely recognized Periodic Table in 1869, and since then, it has been a fundamental tool in the field of chemistry. Understanding the Periodic Table helps us recognize patterns and trends among elements, enabling us to predict their behaviors and form a solid foundation for further scientific studies.
Periods and Groups: The Periodic Table is divided into periods (rows) and groups (columns). Each period represents the number of electron shells an atom of an element possesses, while each group indicates elements with similar chemical properties due to their shared electron configuration.
Full Names and Symbols of Elements:
- Hydrogen (H)
- Helium (He)
- Lithium (Li)
- Beryllium (Be)
- Boron (B)
- Carbon (C)
- Nitrogen (N)
- Oxygen (O)
- Fluorine (F)
- Neon (Ne)
... and so on, up to 118 elements (as of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021).
Here are some notable elements:
- Sodium (Na)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Aluminum (Al)
- Silicon (Si)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Sulfur (S)
- Chlorine (Cl)
- Potassium (K)
- Calcium (Ca)
Transition Metals: The Periodic Table also includes transition metals, which are elements found in the d-block. They possess unique properties and often form colorful compounds. Here are a few examples:
- Iron (Fe)
- Copper (Cu)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Silver (Ag)
- Gold (Au)
Lanthanides and Actinides: The elements found in the f-block, also known as lanthanides and actinides, are mostly synthetic and have fascinating properties. A couple of examples are:
- Uranium (U)
- Plutonium (Pu)
Conclusion:
Understanding the Periodic Table and the full names and symbols of elements is essential for any aspiring scientist or chemistry enthusiast. It lays the groundwork for further exploration and discovery in the world of science. If you're eager to learn more and want to access additional educational resources, SchoolMyKids is here to support you on your academic journey. Visit their website for an array of valuable tools and materials that will make your learning experience even more enriching and enjoyable. Happy exploring!














