Sinusitis (Sinus Infections): Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Sinusitis (Sinus Infections): Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
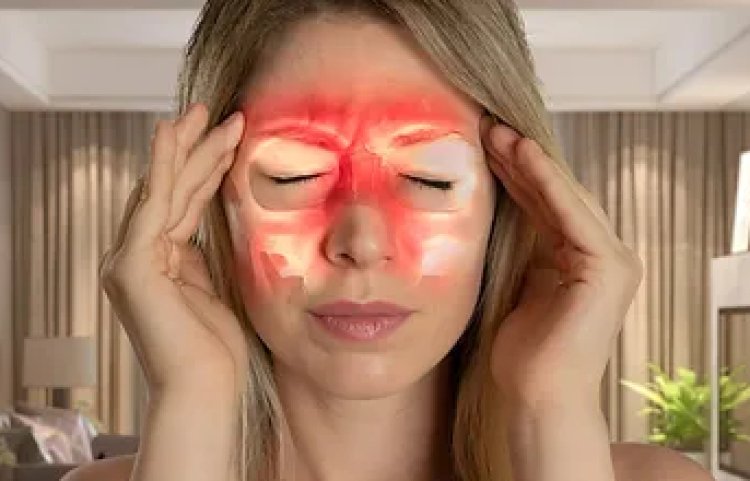
Sinusitis, commonly known as a sinus infection, is a condition that occurs when the tissues lining the sinuses become inflamed or swollen. This can lead to uncomfortable symptoms such as nasal congestion, facial pain, and headaches. Sinusitis is a common condition that affects millions of people each year, and it can be caused by various factors, including infections, allergies, and environmental irritants. In this article, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sinusitis.
Understanding Sinusitis
The sinuses are air-filled spaces located within the bones of the face and skull. They are connected to the nasal passages and help produce mucus that keeps the nasal passages moist and traps dust, pollutants, and other particles. When the sinuses become blocked or filled with fluid, they can become infected, leading to sinusitis.
Causes of Sinusitis
Sinusitis can be triggered by several factors, including:
-
Viral Infections:
- The most common cause of sinusitis is a viral infection, such as the common cold. When the virus infects the upper respiratory tract, it can cause inflammation and swelling in the sinuses, leading to blockage and infection.
-
Bacterial Infections:
- In some cases, a bacterial infection can develop following a viral infection. Bacterial sinusitis is more likely if symptoms persist for more than 10 days or worsen after initial improvement.
-
Allergies:
- Allergic reactions to pollen, dust mites, mold, or pet dander can cause inflammation in the nasal passages and sinuses, leading to sinusitis.
-
Fungal Infections:
- Although less common, fungal infections can cause sinusitis, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic sinusitis.
-
Structural Issues:
- Structural problems in the nose, such as a deviated septum or nasal polyps, can obstruct the sinuses and lead to infections.
-
Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to cigarette smoke, pollutants, or chemicals can irritate the sinuses and increase the risk of sinusitis.
Symptoms of Sinusitis
The symptoms of sinusitis can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Nasal Congestion: A blocked or stuffy nose is a hallmark symptom of sinusitis.
- Facial Pain or Pressure: Pain or pressure in the forehead, cheeks, or around the eyes is common, and it may worsen when bending over.
- Headache: Sinus headaches are often described as a deep, throbbing pain in the forehead or around the eyes.
- Thick Nasal Discharge: A thick, yellow or green discharge from the nose is typical of sinusitis.
- Reduced Sense of Smell or Taste: Sinus congestion can affect the sense of smell and taste.
- Cough: A persistent cough, particularly at night, may occur as mucus drains down the back of the throat (postnasal drip).
- Fever: A low-grade fever may accompany a sinus infection, especially in cases of bacterial sinusitis.
- Bad Breath: Halitosis (bad breath) can result from infected mucus in the sinuses.
Treatment Options for Sinusitis
Treatment for sinusitis depends on the cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common treatment approaches:
-
Home Remedies:
- Saline Nasal Spray: Using a saline nasal spray can help clear nasal congestion and promote mucus drainage.
- Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam from a hot shower or a bowl of hot water can help open the sinuses and relieve congestion.
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the face can reduce pain and pressure in the sinuses.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids can help thin mucus and promote drainage.
-
Medications:
- Decongestants: Over-the-counter decongestants can reduce nasal congestion, but they should be used for only a few days to avoid rebound congestion.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help relieve pain and reduce fever.
- Antibiotics: If bacterial sinusitis is suspected, a doctor may prescribe antibiotics. It's important to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the infection is fully treated.
- Antihistamines: If allergies are contributing to sinusitis, antihistamines can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
-
Surgical Intervention:
- Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: In cases of chronic or recurrent sinusitis that does not respond to other treatments, endoscopic sinus surgery may be recommended. This minimally invasive procedure involves removing blockages or correcting structural issues to improve sinus drainage.
Prevention of Sinusitis
Preventing sinusitis involves reducing your exposure to triggers and maintaining good sinus health:
- Avoid Allergens: Minimize exposure to allergens by keeping windows closed during high pollen seasons, using air purifiers, and washing bedding regularly.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently to reduce the risk of infections.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep mucus thin and prevent blockages.
- Use a Humidifier: Adding moisture to the air with a humidifier can help keep the nasal passages and sinuses hydrated.
- Quit Smoking: Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke, as it can irritate the sinuses.
Conclusion
Sinusitis is a common and often uncomfortable condition that can disrupt daily life. Understanding the causes and symptoms of sinus infections is crucial for seeking timely treatment and preventing complications. Whether it's a viral, bacterial, or allergic cause, appropriate treatment can help alleviate symptoms and promote recovery. For chronic cases, working with a healthcare provider to identify and address underlying issues is key to long-term relief.
For more health information and tips, visit MedyBlog.















