What is the Use of Lecithin in Liposomes?
Liposomes, the tiny spherical vesicles used to deliver nutrients and drugs to specific cells in the body, have become a revolutionary tool in the fields of nutrition, medicine, and skincare.
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
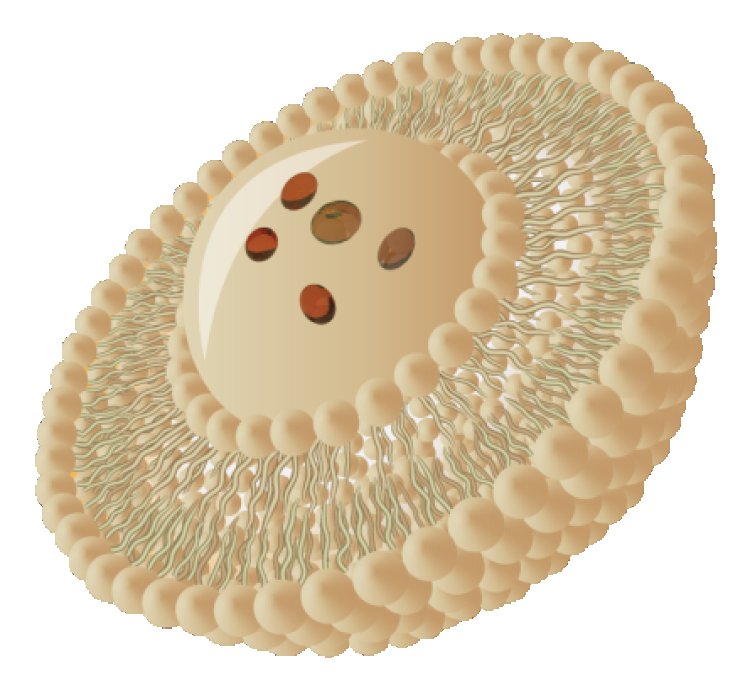
One of the critical components in the creation of liposomes is lecithin, a naturally occurring fatty substance that plays a significant role in ensuring the stability and effectiveness of liposomal formulations. Lecithin’s unique properties make it an essential building block for creating liposomes, especially in the realm of advanced delivery systems for both dietary supplements and pharmaceuticals. This blog will explore the role of lecithin in liposomes, how it works, and why sunflower lecithin-based liposomes have become a popular choice.
What is Lecithin?
Lecithin is a type of phospholipid, a class of fats that are a key structural component of cell membranes. It can be derived from various natural sources, including eggs, soybeans, and sunflowers. In the human body, lecithin is found in tissues and helps in maintaining cell structure, aiding in fat metabolism, and supporting brain and liver health.
Lecithin is an emulsifier, meaning it has the ability to mix water and fat, which typically don’t blend. This emulsifying property is critical in many food products and in the creation of liposomes. Lecithin consists of both hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) components, making it the perfect material for forming the membrane of liposomes, which encapsulates both water-soluble and fat-soluble substances.
What Are Liposomes?
Liposomes are microscopic vesicles made up of phospholipid bilayers that resemble the structure of biological cell membranes. These tiny, spherical structures are used to encapsulate nutrients, vitamins, drugs, or other active compounds, protecting them from degradation and improving their absorption into the body.
Liposomes are especially useful in delivering substances that are poorly absorbed through traditional methods. By protecting the active ingredient and helping it bypass digestive enzymes or harsh conditions in the gastrointestinal tract, liposomes ensure that the compound reaches its target in the body more efficiently. As a result, the bioavailability of the encapsulated nutrient or drug increases, leading to enhanced therapeutic or nutritional effects.
The Role of Lecithin in Liposomes
The formation of liposomes relies on lecithin as a key component because it provides the phospholipids needed to create the bilayer structure of the liposome. The phospholipids in lecithin arrange themselves into a bilayer when placed in an aqueous environment, with the hydrophilic heads facing outwards towards the water and the hydrophobic tails facing inward. This bilayer acts as a barrier, trapping water and soluble compounds inside, while allowing fat-soluble compounds to embed within the membrane itself.
Lecithin provides several key functions in liposomes:
-
Stability: Lecithin helps form a stable bilayer membrane that can protect the encapsulated compound from external factors such as enzymes, oxidation, or light, thereby preventing degradation of the active ingredient.
-
Biocompatibility: Since lecithin is a natural component of cell membranes, liposomes made from lecithin are biocompatible and non-toxic, making them safe for use in the body. The body recognizes these liposomes as familiar structures, which helps them merge with cell membranes, facilitating the delivery of the encapsulated substance.
-
Encapsulation Efficiency: Lecithin’s ability to encapsulate both water-soluble and fat-soluble compounds makes it a versatile ingredient in liposome production. This ensures a wide range of nutrients or drugs can be effectively delivered to the body.
-
Improved Absorption: Lecithin-based liposomes enhance the bioavailability of nutrients or drugs, allowing them to be absorbed more easily by the cells and tissues. This is particularly important for substances that are normally poorly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.
Sunflower Lecithin Based Liposomes
While lecithin can be sourced from several plants and animals, sunflower lecithin has gained immense popularity, especially in the creation of liposomes. Sunflower lecithin-based liposomes offer several advantages over other types of lecithin, particularly soy-based lecithin, which has been widely used in the past.
-
Non-GMO and Allergen-Free: Sunflower lecithin is naturally free from genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and is not associated with common allergens like soy. This makes sunflower lecithin-based liposomes an attractive option for people with soy allergies or sensitivities, as well as those who prefer non-GMO products.
-
Cleaner Extraction Process: Sunflower lecithin is typically extracted through a mechanical process rather than the chemical solvents used in soy lecithin extraction. This results in a purer and cleaner product, which is highly desirable for consumers looking for natural and organic options in supplements and skincare products.
-
Sustainability: Sunflowers are a sustainable crop with minimal environmental impact, making sunflower lecithin a more eco-friendly option compared to soy lecithin. This appeals to the growing number of environmentally-conscious consumers.
-
Health Benefits: Sunflower lecithin has a higher phosphatidylcholine content, an essential component in cell membrane health, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity and function of cells. This makes sunflower lecithin-based liposomes even more effective in supporting cellular health and nutrient delivery.
Applications of Lecithin in Liposomal Supplements
Lecithin-based liposomes are widely used in the dietary supplement industry to improve the absorption of vitamins, minerals, and other bioactive compounds. Some popular liposomal supplements include:
-
Liposomal Vitamin C: Vitamin C is notoriously difficult to absorb in high quantities when taken orally. Liposomal vitamin C formulations, made with lecithin, can enhance absorption and improve the vitamin's immune-boosting and antioxidant effects.
-
Liposomal Glutathione: Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that helps neutralize free radicals in the body. Liposomal delivery helps protect glutathione from degradation in the digestive system, ensuring more of the active compound reaches the bloodstream.
-
Liposomal Curcumin: Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, is poorly absorbed when consumed as a regular supplement. Liposomal curcumin, formulated with lecithin, enhances its absorption and provides stronger anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits.
Conclusion
Lecithin plays a crucial role in the creation and function of liposomes, offering improved stability, biocompatibility, and absorption of encapsulated nutrients and drugs. Among lecithin types, sunflower lecithin-based liposomes stand out for their natural, allergen-free, and sustainable properties. As liposomal supplements continue to grow in popularity, lecithin will remain a key player in enhancing the effectiveness and bioavailability of these advanced formulations, making it a cornerstone of modern health and wellness products.















