USA comprehensive overview of Dyshidrotic eczema
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
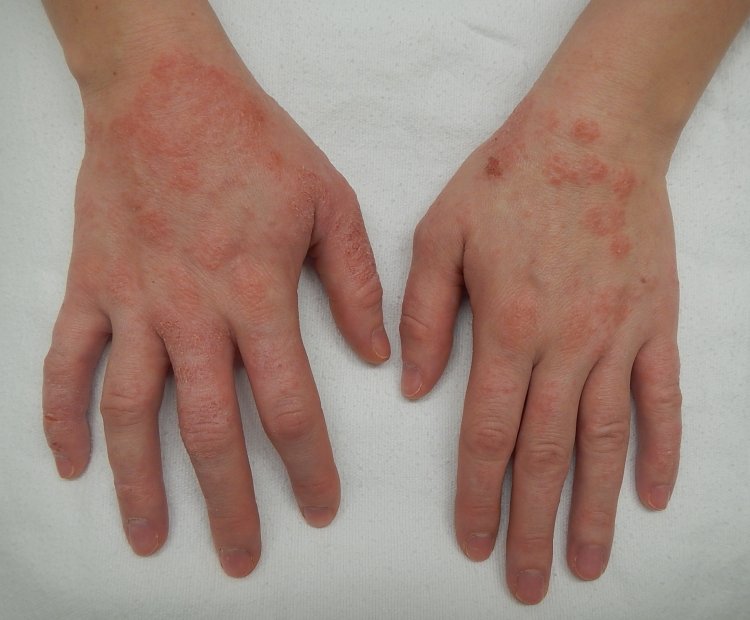
Dyshidrotic eczema, also known as pompholyx or dyshidrosis, is a type of eczema that affects the hands and feet. It is characterized by small, intensely itchy blisters that typically appear on the sides of the fingers, palms, and soles of the feet.
Symptoms
- Blisters: Small, fluid-filled blisters that usually appear in clusters.
- Itching and Burning: Intense itching and sometimes a burning sensation.
- Cracking and Peeling: Once the blisters dry out, they can lead to skin cracking, peeling, and possibly painful fissures.
- Redness and Inflammation: The affected areas can become red, swollen, and inflamed.
Causes
The exact cause of dyshidrotic eczema is unknown, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Allergies: Individuals with a history of atopic dermatitis or other allergic conditions are more prone.
- Stress: Emotional stress is often reported as a trigger.
- Sweating: Excessive sweating, particularly on the hands and feet, may play a role.
- Irritants: Exposure to certain substances like metals (nickel, cobalt), soaps, and detergents can trigger flare-ups.
- Seasonal Changes: It is more common in warmer weather or during times of high humidity.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is typically made based on the clinical appearance of the skin. A dermatologist may conduct:
- Physical Examination: Observing the characteristic blisters and patterns.
- Patch Testing: To identify possible allergens.
- Biopsy: Rarely, a skin biopsy might be performed to rule out other conditions.
Treatment
While there is no cure for dyshidrotic eczema, treatments focus on managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups:
- Topical Steroids: To reduce inflammation and itching.
- Moisturizers: To keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness and cracking.
- Cold Compresses: To alleviate itching and reduce swelling.
- Antihistamines: To help control itching.
- Phototherapy: In some cases, light therapy might be beneficial.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Stress management techniques, avoiding known triggers, and wearing protective gloves or footwear.
Prevention
Preventative strategies include:
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding allergens or irritants.
- Skincare Routine: Regularly moisturizing hands and feet with emollient-rich creams.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or other relaxation methods.
- Protective Measures: Using gloves when handling irritants, and choosing breathable footwear to reduce sweating.
Dyshidrotic eczema can be a persistent and uncomfortable condition, but with proper management, symptoms can be controlled, and quality of life can be improved. If you suspect you have dyshidrotic eczema, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. https://www.eonlinepharmacystore.com














![Noots Focus Reviews [Truth Exposed 2025] 100% Legal Solution!](https://blog.rackons.in/uploads/images/202501/image_380x226_678e3dd58cca6.jpg)
