Cardboard Price Chart: An In-Depth Analysis
Cardboard Price Chart
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
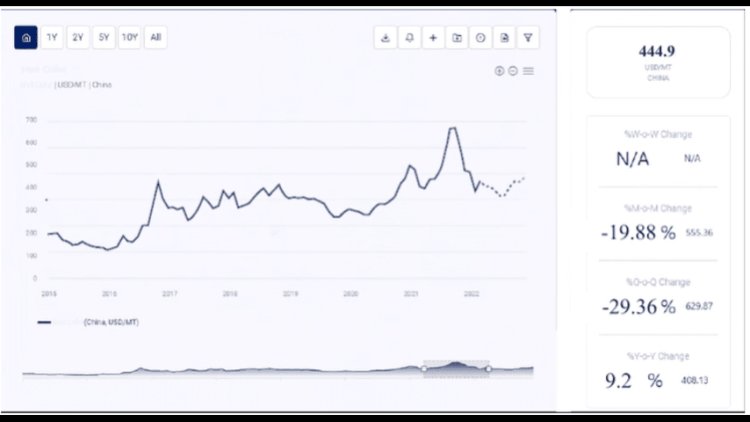
Cardboard, also known as corrugated fiberboard, is a crucial material in the packaging industry. It is widely used for its strength, lightweight nature, and recyclability. The price of cardboard is subject to various factors, including raw material costs, demand and supply dynamics, energy prices, and environmental regulations. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of cardboard price chart, examining historical data, key factors influencing price changes, and future outlooks.
Historical Price Trends
Long-Term Trends
Over the past several decades, the price of cardboard has generally followed an upward trajectory. This long-term increase can be attributed to rising demand for packaging materials, driven by the growth of e-commerce, industrial production, and consumer goods. However, this trend has been marked by periods of volatility due to fluctuations in raw material costs and economic conditions.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/cardboard-price-trends/pricerequest
Periodic Volatility
Cardboard prices are known for periodic volatility, which can be influenced by factors such as changes in raw material supply, shifts in demand, and economic cycles. For instance, during economic downturns, demand for packaging materials often decreases, leading to lower prices. Conversely, during economic expansions, increased industrial activity and consumer spending drive up demand and prices.
Key Factors Influencing Cardboard Prices
Raw Material Costs
-
Pulp and Paper Prices: The primary raw materials for cardboard production are pulp and recycled paper. Fluctuations in the prices of these raw materials can significantly impact cardboard prices. Factors such as supply chain disruptions, changes in global demand, and environmental regulations affecting pulp and paper production can lead to price volatility.
-
Recycling Rates: The availability and cost of recycled paper, a major component in cardboard production, play a crucial role in determining prices. Higher recycling rates can help stabilize raw material costs, while shortages or increased demand for recycled paper can drive up prices.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
-
E-Commerce Growth: The rapid growth of e-commerce has been a major driver of increased demand for cardboard packaging. Online retailers require large quantities of cardboard for shipping and packaging products, contributing to higher prices.
-
Industrial Production: Industrial activity, particularly in sectors such as manufacturing, food and beverage, and consumer goods, influences the demand for cardboard. Economic growth and industrial expansion typically lead to increased demand and higher prices.
Energy Costs
Cardboard production is energy-intensive, with significant energy consumption required for processes such as pulping, papermaking, and corrugating. Changes in energy prices, particularly electricity and natural gas, can impact production costs and, consequently, cardboard prices. Regions with lower energy costs may have a competitive advantage in cardboard production.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations aimed at reducing waste, promoting recycling, and curbing carbon emissions can affect cardboard production costs. For example, stricter regulations on waste management and recycling can increase the cost of raw materials and production processes. Additionally, policies promoting sustainable packaging can drive demand for recycled cardboard, influencing prices.
Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events, such as trade disputes, tariffs, and international conflicts, can disrupt supply chains and impact cardboard prices. For instance, trade tensions between major paper and cardboard producing countries can lead to supply shortages and price increases. Geopolitical stability is crucial for maintaining a stable supply of raw materials and finished products.
Recent Price Trends
Short-Term Price Movements
In recent years, cardboard prices have experienced significant short-term fluctuations. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021 led to disruptions in supply chains, changes in consumer behavior, and fluctuations in demand. Initially, lockdowns and reduced industrial activity led to lower demand and prices. However, as e-commerce surged and supply chains adjusted, demand for cardboard increased, leading to higher prices.
Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on the cardboard market. Lockdowns and movement restrictions disrupted supply chains, leading to temporary shortages of raw materials and increased prices. Additionally, the surge in e-commerce and home delivery services drove up demand for cardboard packaging. The pandemic highlighted the importance of supply chain resilience and the need for efficient recycling systems.
Case Studies of Major Cardboard Markets
United States
The United States is one of the largest producers and consumers of cardboard. The U.S. market is characterized by significant demand from the e-commerce sector, industrial production, and consumer goods. Recent trends in the U.S. cardboard market have been influenced by changes in recycling rates, energy costs, and environmental regulations. For example, policies promoting recycling and sustainable packaging have driven demand for recycled cardboard.
China
China is a major producer and consumer of cardboard, with a significant portion of its production used for domestic consumption and exports. The Chinese cardboard market is influenced by factors such as industrial production, export demand, and environmental regulations. In recent years, China's efforts to improve environmental sustainability and reduce waste have impacted the availability and cost of raw materials for cardboard production.
Europe
Europe is a significant producer and consumer of cardboard, with major production centers in countries such as Germany, France, and Italy. The European cardboard market is influenced by environmental regulations, recycling policies, and demand from various industries. The European Union's focus on sustainability and circular economy initiatives has driven demand for recycled cardboard and influenced market dynamics.
The Impact of Climate Change on Cardboard Production
Climate change poses a significant risk to cardboard production globally. Changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and the frequency of extreme weather events can impact raw material supply and production processes. Key impacts of climate change on cardboard production include:
-
Resource Availability: Changes in climate conditions can affect the availability of raw materials, such as wood pulp and recycled paper. Droughts, floods, and other extreme weather events can disrupt the supply of these materials, leading to price increases.
-
Regulatory Changes: Governments may implement stricter environmental regulations to combat climate change, impacting production costs and supply chains. Policies promoting sustainable forestry and waste management can affect the availability and cost of raw materials.
-
Sustainability Initiatives: The cardboard industry is increasingly focusing on sustainability initiatives, such as reducing carbon emissions and promoting recycling, to mitigate the impact of climate change. These initiatives can influence production costs and market dynamics.
Technological Innovations in Cardboard Production
Technological advancements are transforming the cardboard industry, offering solutions to some of the challenges faced by producers. Key innovations include:
-
Recycling Technologies: Improved recycling technologies can increase the supply of recycled paper, reducing the need for primary raw materials and lowering environmental impact. Innovations in sorting, pulping, and deinking processes can enhance the efficiency of recycling operations.
-
Energy Efficiency: Advances in energy-efficient production technologies can reduce production costs and carbon emissions. Technologies such as energy-efficient pulping and papermaking processes can improve the sustainability of cardboard production.
-
Automation and Digitalization: The adoption of automation and digitalization in production processes can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance supply chain resilience. Technologies such as automated sorting and packaging systems can streamline operations and reduce waste.
Future Outlook
Demand Growth
The demand for cardboard is expected to continue growing, driven by factors such as the expansion of e-commerce, industrial production, and consumer goods. Emerging markets, particularly in Asia, are expected to be major drivers of future demand. Additionally, the shift towards sustainable packaging solutions will drive demand for recycled cardboard.
Supply Challenges
Supply challenges, including resource availability, energy costs, and environmental regulations, will continue to impact cardboard prices. Ensuring a stable supply of raw materials and adopting sustainable production practices will be critical for the industry. Investments in recycling infrastructure and sustainable forestry practices will help mitigate supply risks.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements will play a key role in shaping the future of the cardboard industry. Innovations in recycling, energy efficiency, and automation will help producers meet growing demand while addressing environmental and cost challenges. Continued investment in research and development will be essential for maintaining competitiveness and sustainability.
Conclusion
Cardboard prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including raw material costs, supply and demand dynamics, energy prices, environmental regulations, and geopolitical events. Understanding these factors is essential for stakeholders across the cardboard supply chain, from producers to consumers and policymakers. By adopting sustainable practices, investing in technology, and implementing effective policy interventions, it is possible to mitigate price volatility and ensure a stable supply of this critical material. As global challenges like climate change continue to evolve, the cardboard industry must adapt to maintain the delicate balance between supply and demand, ensuring that cardboard remains an affordable and accessible material for various applications worldwide.

 leofrank
leofrank 














