Understanding 3D Printer Parts: Essential Components for Success
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
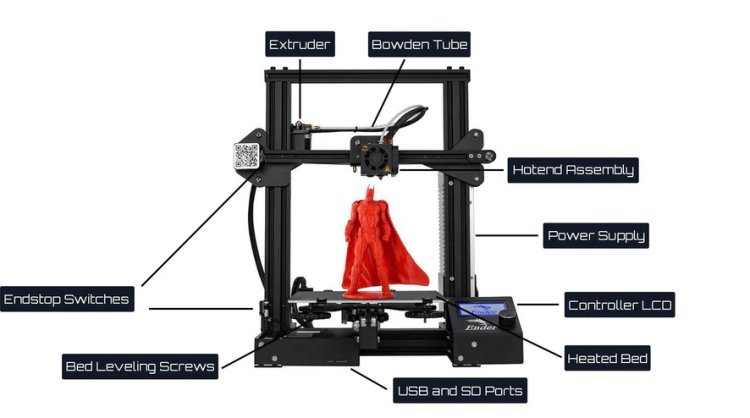
Introduction to 3D Printer Parts
The world of 3D printing has seen explosive growth in recent years, revolutionizing industries by offering a unique combination of speed, precision, and cost-effectiveness. Whether you're a hobbyist, professional, or part of a larger organization, understanding the essential parts of a 3D printer is crucial to maximizing its capabilities and troubleshooting issues that arise during the printing process.
In this article, we'll dive into the main 3D printer parts, their functions, and how they work together to create high-quality prints. Whether you're setting up your first 3D printer or looking to improve your understanding, knowing the role of each part can help optimize your printing experience.
Key Components of a 3D Printer
A 3D printer operates through a combination of various components, each working together in harmony to transform digital designs into physical objects. Let’s look at the core 3D printer parts and their functions.
1. Extruder
The extruder is one of the most vital parts of any 3D printer. It is responsible for feeding filament into the hotend where it is heated and extruded onto the print bed, forming the object layer by layer.
-
Hot End: The hotend is where the filament melts. It contains a nozzle through which the melted filament is extruded. The temperature is carefully controlled to ensure the filament flows smoothly.
-
Cold End: The cold end of the extruder is responsible for feeding filament into the hot end. It typically includes a stepper motor, gears, and an idler wheel that drive the filament into the heated section.
Issues like clogging, inconsistent extrusion, or poor layer adhesion are often associated with problems in the extruder, making it a crucial component to keep in good condition.
2. Print Bed (Build Platform)
The print bed, also known as the build platform, is where the object is created. As the 3D printer extrudes molten filament, it is deposited layer by layer onto the print bed, which moves downward or upward (depending on the printer model) as the print progresses.
- Heated Print Bed: A heated print bed helps to improve adhesion, prevent warping, and ensure a smooth first layer. Many filament materials, such as ABS, require a heated bed for successful printing.
The print bed's material can vary, with options like glass, aluminum, or magnetic beds, each offering different benefits in terms of adhesion, thermal properties, and ease of use.
3. Stepper Motors
Stepper motors are responsible for moving the 3D printer’s components along the X, Y, and Z axes. These motors are essential for the precision of the 3D printing process, ensuring that every layer is placed in the correct position relative to the previous one.
- X-Axis Motor: Moves the extruder left and right.
- Y-Axis Motor: Moves the print bed forward and backward.
- Z-Axis Motor: Moves the extruder up and down.
Stepper motors operate in tiny increments to ensure precise movements, which is vital for producing accurate and high-quality prints.
4. Endstops/Sensors
Endstops, also known as limit switches, are used to detect the position of the moving parts (X, Y, Z axes) of the 3D printer. They are typically placed at the end of each axis and help the machine know when it has reached its limit, preventing it from moving too far and causing damage.
Some modern 3D printers are equipped with sensors for auto bed leveling to ensure that the print bed is level before printing begins. This helps avoid issues like poor adhesion and uneven first layers.
5. Control Board (Motherboard)
The control board is the brain of the 3D printer. It interprets the commands from the 3D printing software, such as G-code, and translates them into actions for the printer’s motors and other components.
A control board coordinates all aspects of the printer’s operation, including motor movement, temperature control, and communication with the user interface. It’s responsible for converting the 3D model into precise instructions that guide the printer through the printing process.
6. Hotend Cooling Fans
Cooling fans are crucial for regulating the temperature of the hotend and preventing overheating during the printing process. Cooling fans help maintain consistent temperature levels, ensuring that the filament is heated properly and extruded consistently.
- Hotend Fan: Keeps the hotend at the correct temperature, preventing clogs or thermal damage to the extruder.
- Part Cooling Fan: Ensures that the extruded filament cools evenly as it is deposited, especially for materials that are sensitive to temperature changes, like PLA.
Cooling fans help achieve smooth layer bonding and improve print quality, particularly in fine details or overhangs.
7. Power Supply Unit (PSU)
The power supply unit (PSU) is the heart of your 3D printer’s electrical system. It supplies the necessary power to the printer’s motors, heated bed, hotend, and control board. Without a functioning PSU, the printer wouldn’t operate at all.
A quality PSU is essential to ensure that the printer receives a stable and sufficient power supply, especially for printers with heated beds or high-power extruders.
8. Display/Interface (LCD or Touchscreen)
The display or user interface allows you to control your 3D printer, monitor print progress, and make adjustments. Many 3D printers come with LCD screens or touchscreen interfaces that provide options for controlling the temperature, print speed, and other settings.
- LCD Screen: An LCD screen typically provides basic functions and settings.
- Touchscreen Display: A more advanced interface with touch controls, offering a smoother and more intuitive experience. Touchscreens may include features like real-time monitoring, temperature control, and direct file printing.
The display interface makes the 3D printing process more accessible, allowing users to interact with their printer effectively.
How 3D Printer Parts Work Together
The operation of a 3D printer is a carefully coordinated effort between all of its parts. The control board interprets the commands sent from the software, which are translated into movement commands for the stepper motors. The extruder feeds filament into the hotend, which heats it and deposits it onto the print bed. As the print progresses, the bed moves down or the extruder moves up to create each layer.
Sensors and endstops ensure that the printer’s parts remain in the correct position, while cooling fans regulate temperatures for optimal print quality. The entire system works together to produce a 3D object based on a digital design.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Even the best 3D printers can experience issues. Here are a few common problems related to 3D printer parts and tips for fixing them:
- Clogged Extruder: A clogged extruder can cause poor extrusion or missed layers. Clean the extruder nozzle regularly to ensure proper filament flow, and consider using higher-quality filament to avoid clogs.
- Warping: Warping occurs when the print bed is not heated or when the material shrinks during printing. Use a heated bed or adhesive sheets to improve adhesion, especially with materials like ABS.
- Inconsistent Movement: If the printer’s movements are jerky or imprecise, check the stepper motors, belts, and endstops for damage. Tighten or replace any loose components to restore accurate movement.
- Overheating Hotend: If your hotend is overheating, check the cooling fans and ensure that they are functioning correctly. If the hotend continues to overheat, the fan or heat sink may need to be replaced.
Routine maintenance, including cleaning the extruder, checking for loose components, and ensuring the correct settings are used, can prevent most issues from arising.
Conclusion: Maximizing the Potential of 3D Printer Parts
A 3D printer's parts work in tandem to deliver precise, high-quality results. Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional, understanding the critical components of your 3D printer—like the extruder, print bed, control board, and stepper motors—will empower you to troubleshoot issues, improve print quality, and extend the lifespan of your machine.
Regular maintenance of 3D printer parts ensures consistent performance, and upgrades or replacements may be necessary over time to keep up with new printing techniques. Whether you're printing prototypes, custom parts, or intricate designs, a solid understanding of 3D printer parts will enhance your 3D printing experience.













