Spinal Fusion: A Comprehensive Guide to Treating Spinal Disorders
Explore spinal fusion, a surgical procedure for treating spinal disorders such as degenerative disc disease and scoliosis. Learn about its benefits, risks, and recovery. For advanced care, consider Sir HN Reliance Hospital Mumbai.
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
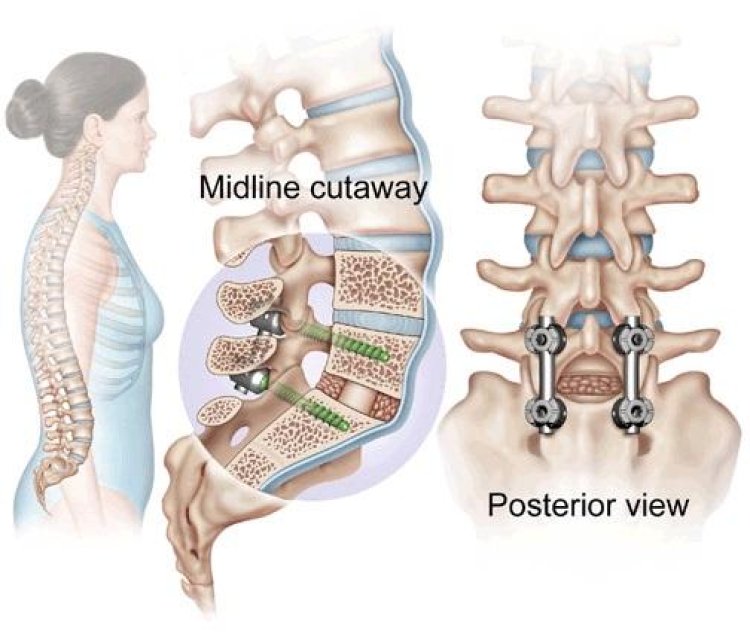
Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure designed to address various spinal disorders by joining two or more vertebrae together to form a single, solid bone. This technique is commonly used to treat conditions such as degenerative disc disease, spinal fractures, scoliosis, and spinal instability. By stabilizing the affected segments of the spine, spinal fusion can help alleviate pain, improve function, and prevent further spinal deformity. For expert care and advanced treatment options, Sir HN Reliance Hospital Mumbai offers specialized spinal fusion procedures. This article explores the principles behind spinal fusion, its indications, procedure, benefits, risks, and recovery process.
Understanding Spinal Fusion
The primary goal of spinal fusion is to eliminate motion between vertebrae in order to stabilize the spine and relieve pain. The procedure involves the use of bone grafts, which can be obtained from the patient (autograft), a donor (allograft), or synthetic materials. These grafts are placed between the vertebrae, and over time, they fuse together with the existing bone to form a single, rigid unit.
Indications for Spinal Fusion
Spinal fusion may be recommended for various spinal conditions, including:
- Degenerative Disc Disease: A condition where the intervertebral discs lose their cushioning ability, causing pain and instability.
- Spinal Fractures: Fractures of the vertebrae, often caused by trauma or osteoporosis, which may require stabilization to heal properly.
- Scoliosis: A spinal deformity characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine, which may require fusion to correct or stabilize the curve.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal that compresses the spinal cord or nerves, often requiring fusion to alleviate pressure and stabilize the spine.
- Spondylolisthesis: A condition where one vertebra slips forward over the one below it, leading to instability and pain.
The Spinal Fusion Procedure
Spinal fusion is typically performed under general anesthesia, and the procedure involves several key steps:
-
Preparation and Anesthesia The patient is placed under general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free during the surgery. The surgical team prepares the patient and sterilizes the area of the spine to be operated on.
-
Incision and Exposure A surgical incision is made in the back or neck, depending on the location of the affected vertebrae. The surgeon carefully retracts the surrounding muscles and tissues to access the spine.
-
Removal of Damaged Tissue The surgeon removes any damaged or diseased disc material, bone spurs, or other tissue that is causing pain or nerve compression.
-
Bone Graft Placement Bone graft material is placed between the affected vertebrae. The graft material helps promote the growth of new bone and encourages the fusion of the vertebrae. In some cases, additional implants such as screws, rods, or plates may be used to provide additional support and stability.
-
Closure Once the graft material is in place and any necessary implants are secured, the incision is closed with sutures or staples. The surgical team monitors the patient during the recovery phase to ensure there are no immediate complications.
Benefits of Spinal Fusion
Spinal fusion offers several benefits for patients with spinal disorders:
- Pain Relief: By stabilizing the spine and addressing the underlying cause of pain, spinal fusion can provide significant relief from back and neck pain.
- Improved Function: Stabilizing the spine can improve mobility and function, allowing patients to resume normal activities with less discomfort.
- Prevention of Further Deformity: In conditions like scoliosis or spinal instability, spinal fusion can prevent the progression of deformity and maintain spinal alignment.
Risks and Complications
While spinal fusion is generally safe, it carries some risks and potential complications:
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the incision site or within the spinal area.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding may occur during or after the procedure.
- Nonunion: In some cases, the bone graft may not fuse properly, leading to persistent pain or instability.
- Nerve Damage: There is a risk of nerve injury, which could result in new symptoms such as numbness, weakness, or pain.
- Adjacent Segment Disease: Fusion of one segment may place additional stress on adjacent segments of the spine, potentially leading to new issues in those areas.
Aftercare and Recovery
Postoperative care is crucial for a successful recovery and includes:
- Pain Management: Patients are prescribed pain medications to manage discomfort and facilitate healing.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapy program is often recommended to strengthen the back, improve flexibility, and support the recovery process.
- Activity Restrictions: Patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting, twisting, or other activities that could strain the spine during the initial recovery phase.
- Follow-Up: Regular follow-up visits with the healthcare provider are necessary to monitor the progress of the fusion and address any concerns.
Conclusion
Spinal fusion is a valuable surgical option for treating a variety of spinal disorders, providing pain relief, stability, and improved function. Understanding the procedure, its benefits, risks, and recovery process can help patients make informed decisions and work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve the best possible outcomes. With advancements in surgical techniques and technology, spinal fusion continues to be an effective tool in managing spinal conditions and enhancing patients' quality of life.














