Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Revolutionizing Business Processes
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
In the digital age, businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer experiences. Among these innovations, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a game-changing technology. By leveraging software robots (or bots) to perform repetitive, rule-based tasks, RPA enables organizations to streamline operations, minimize errors, and free up human resources for more strategic endeavors.
This comprehensive guide explores the world of RPA, including its definition, benefits, applications, implementation challenges, and future trends.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPA is a technology that uses software bots to emulate and integrate human interactions within digital systems to execute business processes. These bots interact with applications and systems just as humans do, completing tasks like data entry, invoice processing, or responding to emails.
Key Features of RPA:
- Non-Invasive: Works with existing systems without requiring major IT overhauls.
- Rule-Based Automation: Operates on predefined rules and logic.
- Scalability: Easily scaled to handle larger volumes or additional processes.
- 24/7 Operation: Bots can work around the clock without fatigue.
Benefits of RPA
RPA offers a wide range of benefits to businesses across industries:
1. Increased Efficiency
- Automates repetitive tasks, leading to faster process completion.
- Bots can handle large volumes of tasks simultaneously, ensuring scalability.
2. Cost Savings
- Reduces labor costs by automating routine tasks.
- Lowers operational expenses by minimizing errors and rework.
3. Enhanced Accuracy
- Eliminates human errors in data-intensive processes like payroll or inventory management.
4. Improved Employee Satisfaction
- Frees employees from mundane tasks, allowing them to focus on more value-added activities.
5. Compliance and Audit Readiness
- Ensures processes adhere to regulations by executing tasks consistently.
- Creates an audit trail for better transparency.
6. Flexibility and Scalability
- Can adapt to fluctuating workloads and changing business needs.
Applications of RPA
RPA is transforming operations across various industries and functions:
1. Financial Services
- Automates loan processing, account reconciliation, and fraud detection.
- Streamlines customer onboarding processes.
2. Healthcare
- Simplifies patient scheduling, claims processing, and medical billing.
- Reduces administrative burdens on healthcare professionals.
3. Retail
- Manages inventory, order processing, and returns efficiently.
- Enhances customer service through automated chatbots and loyalty program management.
4. Manufacturing
- Streamlines supply chain management and procurement processes.
- Automates quality checks and production reporting.
5. Human Resources
- Facilitates employee onboarding, payroll processing, and leave management.
- Automates resume screening during recruitment.
6. IT Operations
- Enhances system monitoring, ticket resolution, and software updates.
- Supports routine maintenance tasks.
RPA Tools and Platforms
Several RPA tools are available to cater to diverse business needs. Some popular platforms include:
- UiPath: Known for its user-friendly interface and extensive capabilities.
- Automation Anywhere: Offers cloud-native RPA solutions.
- Blue Prism: Focused on enterprise-grade scalability and security.
- Microsoft Power Automate: Seamlessly integrates with the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Kofax RPA: Excels in document-centric process automation.
RPA Implementation Process
Implementing RPA requires a structured approach to ensure successful deployment and return on investment (ROI):
1. Identify Processes for Automation
- Focus on repetitive, rule-based tasks with high volume.
- Conduct a feasibility analysis to determine automation potential.
2. Choose the Right RPA Tool
- Select a tool that aligns with organizational goals, budget, and IT infrastructure.
3. Develop a Proof of Concept (PoC)
- Test the RPA solution on a small scale to evaluate its effectiveness.
4. Design and Build Bots
- Create bots using the selected RPA platform, defining workflows and rules.
5. Test and Validate
- Conduct rigorous testing to ensure accuracy and compliance.
6. Deploy and Monitor
- Launch the bots into the live environment and monitor their performance.
7. Scale and Optimize
- Gradually expand RPA implementation to other processes and refine workflows.
Challenges in RPA Implementation
While RPA offers numerous benefits, organizations may face challenges during implementation:
1. High Initial Investment
- RPA tools and deployment costs can be significant for small businesses.
2. Process Complexity
- Non-standardized or poorly documented processes may hinder automation.
3. Resistance to Change
- Employees may fear job displacement, leading to resistance.
4. Scalability Issues
- Scaling RPA across departments may require additional resources and planning.
5. Maintenance and Updates
- Regular updates and bot maintenance are necessary to ensure optimal performance.
Future Trends in RPA
The evolution of RPA continues to shape its role in the business landscape. Emerging trends include:
1. Intelligent Automation
- Combining RPA with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for smarter bots.
- Enhances decision-making and enables handling of unstructured data.
2. Hyperautomation
- Expanding RPA to cover end-to-end process automation with advanced technologies.
- Focuses on automating every possible task for maximum efficiency.
3. Cloud-Based RPA
- Increasing adoption of cloud platforms for flexibility and cost savings.
- Enables seamless integration with other cloud services.
4. Citizen Developers
- Empowering non-technical employees to build and deploy bots using low-code/no-code platforms.
5. RPA in SMEs
- More small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) adopting RPA as costs decrease.
RPA Use Cases: Real-World Examples
1. Banking and Financial Services
- A leading bank reduced loan processing time by 80% using RPA bots for data extraction and validation.
2. E-Commerce
- An online retailer automated order processing, reducing errors and improving delivery timelines.
3. Telecommunications
- A telecom company implemented RPA to automate customer data updates, enhancing service accuracy.
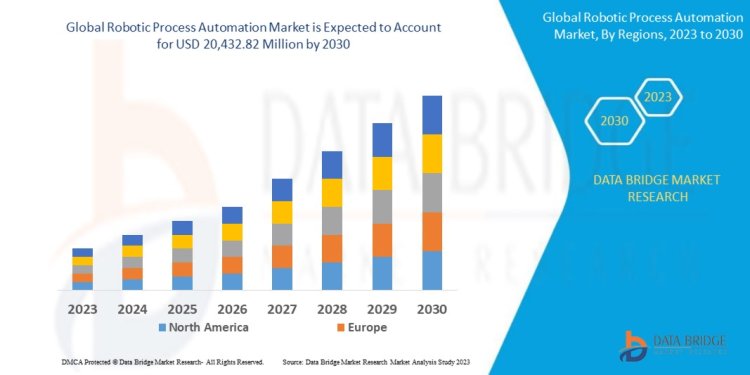
Source: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-robotic-process-automation-market
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation is transforming how businesses operate by automating repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency, and reducing costs. As technology advances, RPA’s integration with AI and other innovations will further expand its capabilities, making it an indispensable tool for organizations across industries. Embracing RPA not only drives operational excellence but also empowers employees to focus on creative and strategic initiatives, paving the way for sustained growth and innovation.