Minimally invasive lumbar spine surgery
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Spine Surgery: A Modern Approach to Back Pain Relief
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
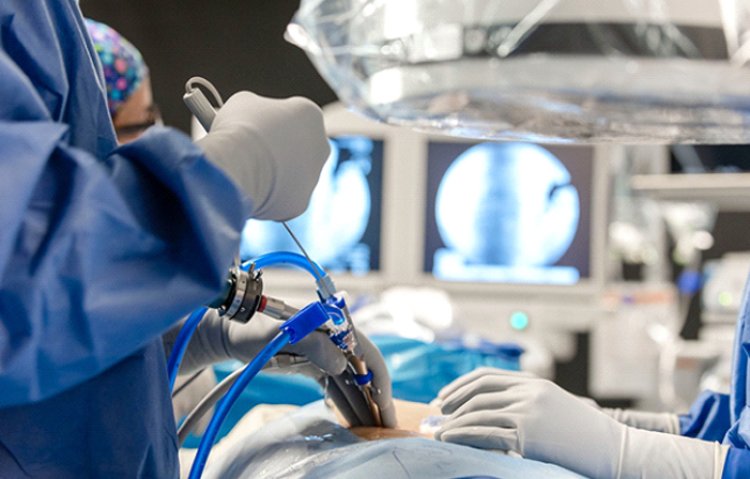
Lower back pain is a pervasive issue, affecting a significant portion of the global population. While conservative treatments like physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications often provide relief, some individuals require surgical intervention to address the underlying cause. Traditionally, lumbar spine surgery involved large incisions, extensive muscle dissection, and prolonged recovery periods. However, advancements in surgical techniques have led to the development of minimally invasive lumbar spine surgery (MIS), offering patients a potentially less disruptive and faster path to recovery.
Understanding Minimally Invasive Lumbar Spine Surgery
MIS techniques aim to accomplish the same goals as traditional open surgery – decompressing nerves, stabilizing the spine, and alleviating pain – but through smaller incisions and with less disruption to surrounding tissues. This is achieved by utilizing specialized instruments, endoscopic cameras, and image guidance systems.
Instead of a long incision that requires significant muscle retraction, MIS typically involves one or more small incisions, often less than an inch in length. These incisions allow surgeons to access the spine through natural tissue planes, minimizing muscle cutting and damage. A tubular retractor is then inserted to create a working channel, providing access to the surgical site. Surgeons then use specialized instruments and microscopic cameras to perform the necessary procedures, guided by real-time imaging.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Lumbar Spine Surgery
The potential advantages of MIS compared to traditional open surgery are numerous and can significantly impact a patient's experience:
- Smaller Incisions: Reduced incision size translates to less scarring and improved cosmetic outcomes.
- Less Muscle Damage: Minimizing muscle dissection leads to less post-operative pain and faster recovery of muscle strength.
- Reduced Blood Loss: Smaller incisions and less tissue disruption result in less blood loss during surgery, potentially reducing the need for blood transfusions.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Due to faster recovery and reduced pain, patients undergoing MIS often require a shorter hospital stay.
- Faster Recovery: With less tissue trauma, patients can typically return to their normal activities more quickly compared to open surgery.
- Reduced Risk of Infection: Smaller incisions can potentially lower the risk of post-operative infections.
Common MIS Procedures
Several lumbar spine conditions can be addressed using MIS techniques, including:
- Microdiscectomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of a herniated disc that is compressing a nerve root.
- Laminectomy/Laminotomy: These procedures involve removing a portion of the lamina (the bony arch of the vertebra) to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots.
- Spinal Fusion: This procedure involves fusing two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine and reduce pain. MIS techniques can be used for fusion procedures, often involving smaller incisions and less muscle disruption.
- Foraminotomy: This procedure widens the foramen (the bony opening through which nerves exit the spinal canal) to relieve nerve compression.
Is MIS Right for You?
While MIS offers several potential benefits, it is not suitable for every patient or every spinal condition. The decision to undergo MIS should be made in consultation with a qualified spine surgeon who can thoroughly evaluate your individual case, including your medical history, the nature of your condition, and the results of imaging studies.
Factors that may influence the suitability of MIS include:
- Complexity of the Spinal Condition: Certain complex spinal deformities or conditions may be better addressed through traditional open surgery.
- Patient's Overall Health: Patients with certain underlying health conditions may not be suitable candidates for MIS.
- Surgeon's Experience: The success of MIS relies heavily on the surgeon's skill and experience with these techniques.
Conclusion
Minimally invasive lumbar spine surgery represents a significant advancement in the treatment of back pain. By utilizing smaller incisions and minimizing tissue disruption, MIS offers the potential for less pain, faster recovery, and improved cosmetic outcomes compared to traditional open surgery. However, it is essential to consult with a qualified spine surgeon to determine if MIS is the right option for your specific condition and to understand the potential risks and benefits involved. As technology continues to advance, MIS is likely to become an increasingly common and effective approach to addressing a wide range of lumbar spine problems, offering patients a path towards a more active and pain-free life.

 danielhicks
danielhicks 















