Lead Acid Battery: An Old Technology Still Going Strong
Despite being one of the oldest types of rechargeable batteries, the lead-acid battery continues to prove its reliability and relevance in modern applications. From powering vehicles and backup power systems to supporting renewable energy storage, this robust technology offers a cost-effective and dependable solution even in today’s advanced energy landscape. In this article, we explore how lead-acid batteries work, their advantages, limitations, and why they remain a trusted choice across various industries.
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
When it comes to dependable energy storage, one name that has stood the test of time is the lead-acid battery. Despite the rise of lithium-ion and other advanced battery technologies, the lead-acid battery continues to play a crucial role in multiple sectors—from automotive to industrial, and even renewable energy systems. Whether you’re powering a car, storing solar energy, or backing up data centers, the lead-acid battery remains a trusted and affordable choice.
One of the most common queries from users is about the lead acid battery full charge voltage, which typically ranges between 12.6V to 12.8V for a fully charged 12V battery. Understanding this not only ensures the battery’s longevity but also helps avoid undercharging or overcharging, both of which can significantly reduce battery life.
A Brief History of Lead-Acid Batteries
The lead-acid battery was invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté. It was the first type of rechargeable battery ever created and remains one of the most widely used today. What makes it so enduring? It’s simple design, low cost, and the ability to deliver high surge currents—ideal for engines and heavy equipment.
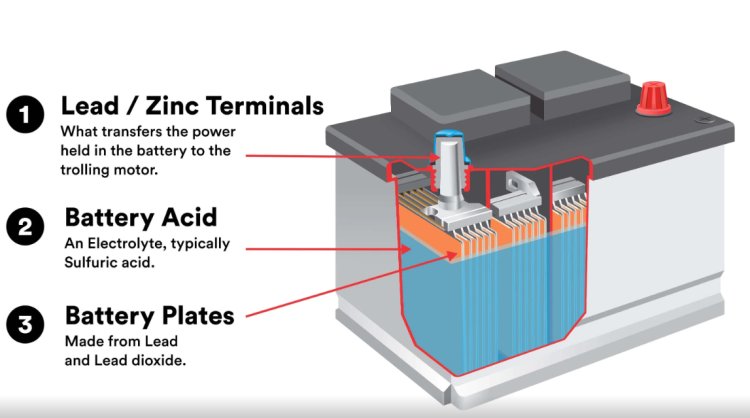
How Does a Lead-Acid Battery Work?
A lead-acid battery consists of lead dioxide (PbO₂) as the positive plate, sponge lead (Pb) as the negative plate, and a diluted sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) solution as the electrolyte. When the battery discharges, a chemical reaction occurs between the lead plates and the sulfuric acid, creating lead sulfate (PbSO₄) and releasing electrical energy. Charging the battery reverses this process, converting the lead sulfate back into lead, lead dioxide, and sulfuric acid.
Types of Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are generally categorized into two main types:
-
Flooded Lead-Acid Batteries (FLA): These are the traditional, liquid-electrolyte batteries that require periodic maintenance such as topping off with distilled water.
-
Valve Regulated Lead-Acid Batteries (VRLA): These are sealed batteries, including AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) and Gel types, designed to be maintenance-free and safer to use in enclosed spaces.
Both types serve different applications, and the choice largely depends on the intended use, budget, and maintenance preferences.
Advantages of Lead-Acid Batteries
Despite newer technologies, lead-acid batteries offer several advantages:
-
Cost-Effective: They are significantly cheaper than lithium-ion and other high-tech batteries.
-
Reliable: With proper care, lead-acid batteries offer consistent performance over several years.
-
High Surge Currents: They can deliver large amounts of power quickly, making them perfect for starting engines.
-
Recyclability: Lead-acid batteries are nearly 100% recyclable, making them an environmentally responsible choice.
Common Applications
Lead-acid batteries are incredibly versatile. Here are some areas where they continue to dominate:
-
Automotive Industry: Almost all gasoline and diesel vehicles use lead-acid batteries to start engines.
-
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): Businesses rely on them to ensure backup power during outages.
-
Renewable Energy Systems: Solar and wind energy setups often use deep-cycle lead-acid batteries for energy storage.
-
Electric Vehicles and Golf Carts: Some older or economy models use them as a low-cost alternative to newer technologies.
Charging and Maintenance
Proper charging is essential for prolonging the lifespan of a lead-acid battery. Overcharging can cause the electrolyte to evaporate, while undercharging leads to sulfation, a condition that limits the battery's capacity. Always use a charger that matches the battery’s voltage and follow manufacturer guidelines.
Regular maintenance includes:
-
Checking and topping off electrolyte levels (for flooded batteries).
-
Cleaning terminals to prevent corrosion.
-
Ensuring the battery is fully charged before storing it for long periods.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
One of the strongest points in favor of lead-acid batteries is their recyclability. The lead, plastic, and acid can all be reclaimed and reused. In fact, lead-acid batteries are among the most recycled products in the world, with a recycling rate exceeding 95%. This makes them a more environmentally sustainable option compared to many modern battery types that are harder to recycle.
Limitations to Consider
While lead-acid batteries offer many advantages, they aren’t perfect. Here are a few limitations:
-
Weight and Size: They are heavier and bulkier than modern alternatives.
-
Lower Energy Density: Compared to lithium-ion, lead-acid batteries store less energy per unit of weight.
-
Shorter Lifespan: They typically last fewer cycles than more advanced battery chemistries.
Why They Still Matter Today
So, why are lead-acid batteries still widely used? The answer lies in their balance of cost, reliability, and performance. For many applications, especially where budget and safety are priorities, lead-acid batteries remain the most logical and effective choice. Until the cost and recyclability of lithium and other alternatives improve significantly, lead-acid batteries will likely retain their relevance in various sectors.
Final Thoughts
The lead-acid battery might not be the most cutting-edge technology today, but it certainly is one of the most reliable. With over 150 years of proven performance, it continues to serve as a dependable power source across the globe. Whether you’re a car owner, a solar enthusiast, or someone looking for reliable backup power, the lead-acid battery deserves a spot on your list.














