How Much Time Does a Brain Tumor Take to Grow?
If you’re seeking expert care for brain tumors, Krishna Shalby Hospital offers state-of-the-art diagnostics and treatment options to address these challenging conditions effectively.
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
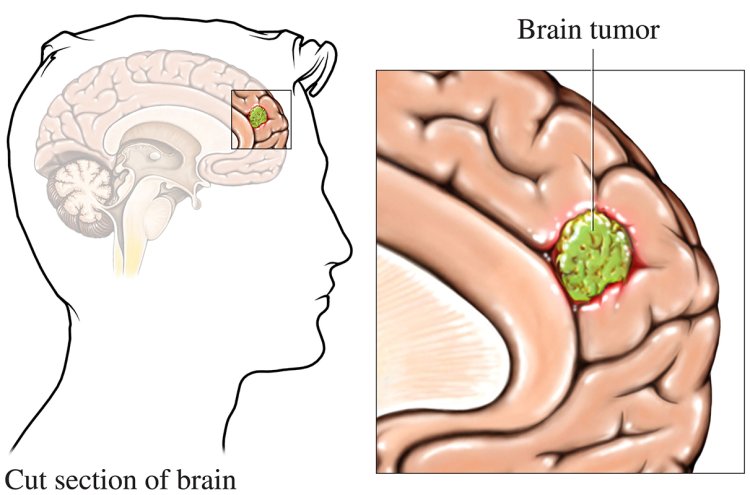
Brain tumors are complex medical conditions that vary significantly in terms of growth rate, size, and symptoms. Some brain tumors grow slowly over years, while others develop rapidly, leading to noticeable symptoms in a short time. Understanding how long a brain tumor can take to grow is essential for early detection and treatment. If you’re seeking expert care for brain tumors, Krishna Shalby Hospital offers state-of-the-art diagnostics and treatment options to address these challenging conditions effectively.
This article will explore the growth rates of different types of brain tumors, the factors that influence their growth, and the importance of early detection for better outcomes.
Understanding Brain Tumor Growth
Brain tumors develop when abnormal cells begin to grow uncontrollably in the brain, forming a mass or lesion. The rate at which these tumors grow depends on several factors, including the type of tumor, its location, and its classification (benign or malignant). Brain tumors are categorized into two broad categories:
1. Benign Tumors
- Growth Rate: Benign tumors are typically slow-growing and non-cancerous. They can take several months or even years to reach a significant size.
- Examples: Meningiomas, pituitary adenomas, and schwannomas.
- Characteristics: These tumors often do not spread to other areas of the brain but can still cause issues by pressing on nearby structures, leading to symptoms.
2. Malignant Tumors
- Growth Rate: Malignant tumors tend to grow rapidly and invade surrounding brain tissues. They may cause severe symptoms within weeks or months of development.
- Examples: Glioblastomas, anaplastic astrocytomas, and metastatic brain tumors.
- Characteristics: These tumors often require aggressive treatment, as they can spread to other parts of the body.
Factors Affecting Brain Tumor Growth
Several factors influence the speed at which a brain tumor grows:
1. Tumor Type
- Different types of brain tumors grow at different rates. For instance, glioblastomas grow very quickly, while meningiomas may remain stable for years.
- The molecular and genetic characteristics of the tumor cells also play a role in how quickly a tumor develops.
2. Location
- Tumors located in critical areas of the brain may grow faster due to their proximity to essential brain functions. However, tumors located in areas where they cause less immediate harm may grow more slowly.
3. Tumor Grade
- The grade of the tumor refers to how abnormal the tumor cells are. Higher-grade tumors (malignant) tend to grow faster and spread more aggressively than lower-grade tumors (benign).
- Tumor grading is an important factor that helps determine the treatment approach and prognosis.
4. Age and Overall Health
- Younger individuals may experience faster tumor progression due to their body’s active cellular division. Conversely, older adults may have slower tumor growth due to slower metabolic rates.
- An individual’s overall health, immune system function, and genetic factors can also influence tumor growth rates.
5. Tumor Size
- Small tumors may grow unnoticed for a longer time. As they enlarge, symptoms become more apparent, prompting medical attention.
- Large tumors can create significant pressure on surrounding brain structures, leading to rapid symptom onset.
How Long Do Different Brain Tumors Take to Grow?
1. Glioblastoma
- Growth Rate: Glioblastomas are one of the fastest-growing and most aggressive brain tumors. They can double in size within weeks to a few months.
- Symptoms: Due to their rapid growth, they often cause significant symptoms like headaches, seizures, and neurological deficits within a short time.
2. Meningioma
- Growth Rate: Meningiomas are typically slow-growing tumors that can take several years to reach a size large enough to cause symptoms.
- Symptoms: Depending on the tumor’s size and location, symptoms can develop gradually over time.
3. Pituitary Adenomas
- Growth Rate: These tumors usually grow slowly, and many patients remain asymptomatic for years.
- Symptoms: When they cause symptoms, it’s often due to hormone imbalances or pressure on surrounding structures.
4. Oligodendrogliomas
- Growth Rate: Oligodendrogliomas are typically slow-growing, but they can become more aggressive over time.
- Symptoms: Patients may experience seizures, headaches, or cognitive changes as the tumor increases in size.
5. Astrocytomas
- Growth Rate: Low-grade astrocytomas may take years to grow, while high-grade (anaplastic) astrocytomas grow much more quickly.
- Symptoms: Symptoms depend on the location of the tumor but may include headaches, personality changes, or motor deficits.
6. Metastatic Brain Tumors
- Growth Rate: Tumors that spread from other parts of the body to the brain (e.g., lung, breast, or colon cancer) tend to grow rapidly. They often appear after the primary tumor has been growing for a while.
- Symptoms: Symptoms can develop quickly, particularly if the metastatic tumors cause swelling or bleeding in the brain.
Early Detection and the Importance of Monitoring Growth
The sooner a brain tumor is detected, the sooner appropriate treatment can be started. Although some tumors may not present symptoms for months or years, many signs, such as persistent headaches, seizures, vision or hearing problems, or changes in behavior, can indicate the presence of a brain tumor.
1. Imaging Tests
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans are essential for detecting brain tumors. Regular imaging may be recommended for individuals with a higher risk of developing brain tumors.
2. Neurological Exams
- Routine neurological exams to monitor symptoms like motor function, reflexes, and cognitive ability can help detect abnormalities early.
3. Monitoring Tumor Growth
- Once diagnosed, the growth of a brain tumor is closely monitored through periodic imaging to assess treatment effectiveness and adjust care plans accordingly.
Treatment Options for Brain Tumors
The growth rate and size of a brain tumor influence the choice of treatment. Options include:
1. Surgical Removal
- Surgery is often the first step, especially for benign tumors. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without damaging healthy brain tissue.
2. Radiation Therapy
- Used to shrink tumors, particularly when surgery is not an option or if some tumor cells remain after surgery.
3. Chemotherapy
- Chemotherapy is often employed for malignant tumors and can help stop the tumor from growing and spreading.
4. Targeted Therapy
- Targeted drugs focus on specific molecules within tumor cells to slow growth and reduce the risk of side effects.
5. Immunotherapy
- Immunotherapy aims to strengthen the body’s immune system to fight cancerous cells, providing an innovative approach to treating brain tumors.
Conclusion
The time it takes for a brain tumor to grow can vary significantly, depending on factors such as the type, location, grade, and individual patient characteristics. Benign tumors may take years to grow, while malignant tumors can develop rapidly, leading to symptoms in a matter of weeks or months. Early detection is key, and seeking expert care at Krishna Shalby Hospital Ahmedabad ensures timely diagnosis and advanced treatment options for better outcomes.
If you or a loved one are experiencing unexplained symptoms such as persistent headaches, cognitive changes, or seizures, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional promptly. With timely intervention, the prognosis for many brain tumor patients can be greatly improved.

















