Comparing Hair Fillers to Other Hair Loss Treatments: Minoxidil, Finasteride, and PRP
Explore the world of hair fillers! Discover benefits, types, the procedure, results, risks, costs, and more in our comprehensive topic list.
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
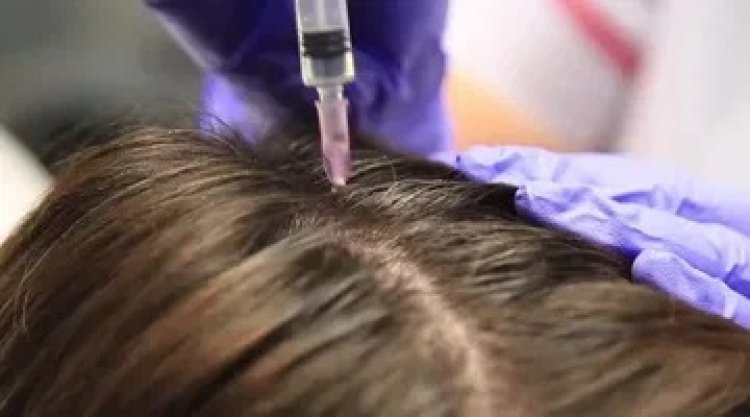
Hair fillers(حشوات الشعر) have gained significant traction as a modern, non-surgical solution for addressing hair thinning and early hair loss. These treatments use active ingredients like peptides, hyaluronic acid, and vitamins to stimulate the scalp and promote healthier, fuller hair. As more people seek effective alternatives to conventional treatments, hair fillers are often compared to other popular options like minoxidil, finasteride, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. Understanding how each treatment works, along with their pros and cons, is essential for choosing the best option for your unique needs.
In this blog, we’ll compare hair fillers with minoxidil, finasteride, and PRP, helping you understand their mechanisms, effectiveness, safety profiles, and suitability for different types of hair loss.
What Are Hair Fillers?
Hair fillers are injectable or topical treatments formulated to rejuvenate the scalp and stimulate dormant or weakened hair follicles. Most filler products include a combination of:
-
Hyaluronic acid: For hydration and skin health
-
Peptides and growth factors: To promote follicle activity
-
Vitamins and amino acids: To nourish hair roots
These ingredients work synergistically to improve hair density, reduce shedding, and enhance scalp vitality. Hair fillers are typically administered in a series of sessions and are considered safe, minimally invasive, and suitable for both men and women.
Minoxidil (Rogaine)
Overview
Minoxidil is a topical treatment available over-the-counter in foam or liquid form. It works by improving blood flow to the hair follicles and prolonging the growth (anagen) phase of the hair cycle.
Effectiveness
Minoxidil is FDA-approved for both men and women and is especially effective for people experiencing androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness). Users typically notice results after 3–6 months of consistent use.
Pros:
-
Easily accessible
-
Simple, non-invasive application
-
Proven to reduce shedding and promote regrowth
Cons:
-
Must be used indefinitely to maintain results
-
Possible side effects include scalp irritation and unwanted facial hair growth
-
Results vary and may be modest
Comparison to Hair Fillers: While minoxidil is easy to use at home, it often delivers slower and less targeted results than hair fillers. Fillers can provide direct nourishment to the follicles, potentially offering faster and more noticeable improvements in hair texture and density.
Finasteride (Propecia)
Overview
Finasteride is an oral medication that works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT)—a hormone linked to hair follicle shrinkage and hair loss.
Effectiveness
Finasteride is highly effective for men with androgenetic alopecia. It significantly reduces hair loss and can promote regrowth in many users. However, it is not approved for use in women, especially those of childbearing age.
Pros:
-
Proven to slow hair loss progression
-
Convenient daily oral tablet
-
Effective in maintaining existing hair
Cons:
-
Risk of sexual side effects (e.g., reduced libido, erectile dysfunction)
-
Results take several months to appear
-
Must be taken continuously
Comparison to Hair Fillers: Hair fillers are a non-hormonal alternative and are generally safer for a wider demographic, including women. They also support scalp health, which finasteride does not address directly. However, finasteride may provide stronger long-term prevention of DHT-related hair thinning in men.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Overview
PRP therapy involves drawing a patient’s own blood, processing it to isolate the platelet-rich plasma, and injecting it into the scalp. Platelets contain growth factors that can stimulate follicle regeneration.
Effectiveness
PRP has shown promising results in treating various forms of hair loss, particularly androgenetic alopecia. It improves hair density, reduces shedding, and can support hair cycle normalization.
Pros:
-
Natural treatment using the patient’s own blood
-
Can promote regeneration without foreign substances
-
Effective when used consistently
Cons:
-
Requires multiple in-clinic sessions
-
May be uncomfortable due to injections
-
Results vary and require ongoing maintenance
Comparison to Hair Fillers: Hair fillers are often considered less invasive than PRP and do not involve blood handling. Additionally, fillers include a broader range of active ingredients targeting hydration, nutrition, and follicle stimulation. However, PRP may appeal to those who prefer autologous (natural) treatments.
Which Treatment Is Best for You?
The right choice depends on your individual goals, type of hair loss, lifestyle, and tolerance for maintenance or side effects. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Treatment | Ideal For | Application | Maintenance | Notable Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hair Fillers | Early to moderate thinning, scalp care | Injections or topical | Every 3–6 months | Requires clinic visits |
| Minoxidil | Mild to moderate androgenetic alopecia | Topical daily | Ongoing daily use | Irritation, lifelong use |
| Finasteride | Male pattern hair loss | Oral daily | Ongoing daily use | Hormonal side effects |
| PRP | Regenerative therapy seekers | Injections (natural) | Every 4–6 months | Cost, discomfort, variable results |
Combining Treatments for Optimal Results
Many specialists recommend combining hair fillers with other therapies for synergistic benefits. For example:
-
Hair fillers + Minoxidil: Improves both internal follicle stimulation and external blood flow.
-
Hair fillers + PRP: Combines synthetic and natural regenerative effects.
-
Hair fillers + Finasteride (for men): Addresses both DHT suppression and follicle nourishment.
A personalized approach, guided by a dermatologist or trichologist, ensures the best outcome for your specific condition.
Conclusion
Hair fillers represent a powerful addition to the arsenal of hair restoration therapies, offering hydration, follicular stimulation, and scalp rejuvenation with minimal side effects. While minoxidil, finasteride, and PRP each offer unique advantages, hair fillers stand out for their versatility, safety profile, and compatibility with both men and women.
If you're exploring treatment options for hair thinning, consult with a qualified professional to assess your hair and scalp condition. The right combination—or even a well-executed filler plan—can help restore your confidence and support long-term hair health.















