Are There Any Risks Associated with Gabapentin?
Discover the potential risks associated with Gabapentin, including common and serious side effects, interactions with other medications, and important safety considerations. Learn how to use Gabapentin safely and what to watch for during treatment.
Share this Post to earn Money ( Upto ₹100 per 1000 Views )
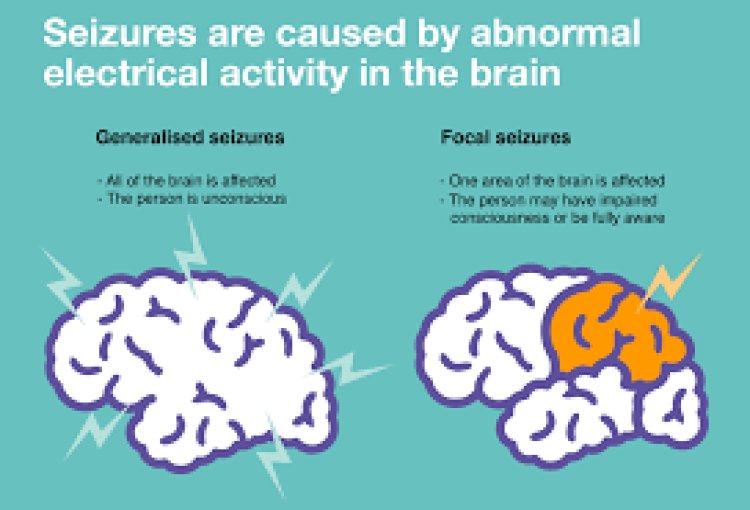
Gabapentin 300mg is a medication commonly prescribed to manage neuropathic pain and seizures. It is also used off-label for various conditions, including anxiety disorders and restless legs syndrome. While it can be effective for these purposes, like all medications, gabapentin comes with its own set of potential risks and side effects. Here’s a detailed overview of the risks associated with gabapentin.
Understanding Gabapentin
Gabapentin 800mg, marketed under various brand names such as Neurontin, is an anticonvulsant and analgesic agent. Its primary mechanism of action involves binding to the voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, which modulates neurotransmitter release. Although originally developed for epilepsy, its use has expanded due to its efficacy in treating neuropathic pain.
Common Side Effects
-
Drowsiness and Fatigue: One of the most common side effects of gabapentin is drowsiness. Patients often report feeling unusually tired or lethargic, which can affect their daily activities and overall quality of life.
-
Dizziness and Balance Issues: Gabapentin can cause dizziness and problems with balance, which increases the risk of falls, especially in older adults.
-
Weight Gain: Some individuals may experience significant weight gain while taking gabapentin, which can contribute to other health issues such as diabetes and cardiovascular problems.
-
Edema: Swelling of the extremities, known as peripheral edema, can occur, leading to discomfort and mobility issues.
-
Gastrointestinal Problems: Nausea, vomiting, and constipation are possible gastrointestinal side effects. These can be particularly troublesome for some patients.
Serious Risks and Adverse Reactions
-
Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may have an allergic reaction to gabapentin. Symptoms of a severe allergic reaction include rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, and trouble breathing. This requires immediate medical attention.
-
Psychiatric Effects: Gabapentin can affect mood and mental health. Some patients may experience mood swings, depression, anxiety, or even suicidal thoughts. Monitoring for changes in mood or behavior is essential.
-
Drug Interactions: Gabapentin can interact with other medications, potentially leading to adverse effects or reduced efficacy. For instance, it may interact with opioids, leading to increased sedation and respiratory depression.
-
Dependency and Withdrawal: Although gabapentin is not classified as a controlled substance, some patients may develop a psychological dependency. Abrupt discontinuation can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, agitation, and insomnia.
-
Cognitive Impairment: There is evidence suggesting that gabapentin may impair cognitive functions, including memory and concentration. This can affect daily functioning and overall quality of life.
Risk Factors and Precautions
-
Pre-existing Conditions: Patients with pre-existing renal conditions need to be cautious with gabapentin use, as it is primarily excreted through the kidneys. Dose adjustments are often required to prevent toxicity.
-
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Gabapentin is classified as a Category C drug, meaning its safety during pregnancy is not well established. It should be used during pregnancy only if the benefits outweigh the risks. Additionally, gabapentin can pass into breast milk, so it should be used with caution in breastfeeding mothers.
-
Elderly Patients: Older adults are at higher risk for side effects like dizziness, drowsiness, and balance issues, which can increase the risk of falls and fractures. Dose adjustments and careful monitoring are recommended.
-
Psychiatric Conditions: Individuals with a history of psychiatric disorders should use gabapentin with caution due to potential effects on mood and behavior.
Managing Risks
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider can help monitor for side effects and adjust the dosage as needed.
-
Gradual Tapering: To minimize withdrawal symptoms, gabapentin should be tapered gradually under the supervision of a healthcare provider if discontinuation is necessary.
-
Medication Review: Regularly reviewing all medications with a healthcare provider can help prevent harmful drug interactions and manage side effects.
-
Patient Education: Educating patients about potential side effects and encouraging them to report any unusual symptoms can lead to timely intervention and management.
Conclusion
Gabapentin can be a highly effective medication for managing certain neurological and pain-related conditions, but it is not without risks. Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, weight gain, and gastrointestinal issues, while more serious risks involve allergic reactions, psychiatric effects, and interactions with other drugs. Careful management, monitoring, and patient education are key to minimizing these risks and ensuring the medication's benefits outweigh its potential downsides. As with any medication, it is crucial for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to tailor their treatment plan to their individual needs and circumstances.













