Amino Acid Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2025: Cost, Process and Market Trends
Explore our comprehensive guide on setting up an amino acid manufacturing plant, covering processes, equipment, market trends, and financial insights.
Introduction
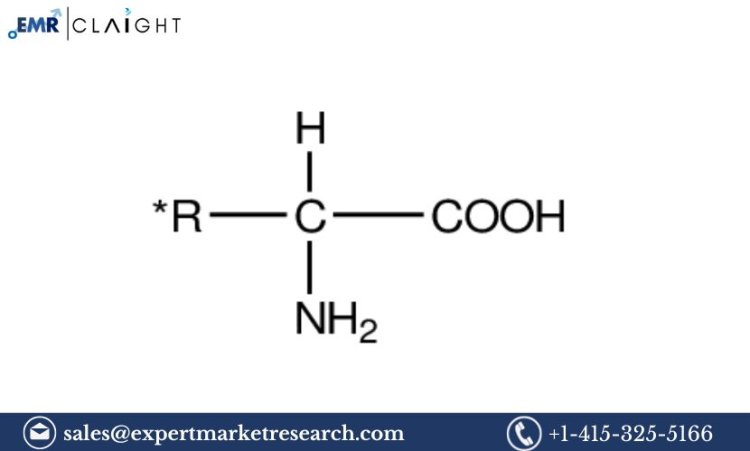
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and their significance extends beyond their role in protein synthesis. They are essential in various biochemical processes and are widely used in food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, animal feed, and agriculture. The demand for amino acids has been growing due to their critical role in enhancing nutrition, improving health, and contributing to sustainable agricultural practices. An Amino Acid Manufacturing Plant represents a strategic opportunity in the global market, especially as industries continue to realise the potential of amino acids in improving human and animal health, boosting crop yields, and promoting overall well-being. This Amino Acid Manufacturing Plant Project Report outlines the essential aspects of setting up an amino acid manufacturing plant, including raw materials, production processes, market trends, equipment, and financial considerations.
Key Applications of Amino Acids
Amino acids are utilised across various sectors, each benefiting from their nutritional and functional properties. Here are the primary industries where amino acids are in demand:
-
Food and Beverage Industry: Amino acids, such as glutamic acid, are used in food processing as flavour enhancers and preservatives. They are also important in nutritional supplements and fortification.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Amino acids are used in the production of drugs, intravenous (IV) solutions, and supplements. They are essential for patients suffering from amino acid deficiencies, metabolic disorders, and other health conditions.
-
Animal Feed: Amino acids like lysine, methionine, and threonine are added to animal feed to improve livestock growth, feed efficiency, and overall health.
-
Cosmetics and Personal Care: Amino acids are used in skin care products for their moisturising and conditioning properties. They are also incorporated into hair care formulations to promote strength and shine.
-
Agriculture: Amino acids are used in agricultural products like fertilisers and plant growth promoters. They help improve crop yield, plant resistance to stress, and overall plant health.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Raw Materials for Amino Acid Manufacturing
Amino acids can be sourced from both natural and synthetic processes. The key raw materials for manufacturing amino acids are:
-
Sugars and Starches: These are often used in fermentation processes, where microorganisms convert them into amino acids.
-
Microorganisms: Specific microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi are employed in the fermentation process to produce amino acids. For example, the production of glutamic acid uses Corynebacterium glutamicum, while Bacillus subtilis is used for producing other amino acids.
-
Enzymes: Enzymatic processes can also be used to produce amino acids by breaking down proteins into their constituent amino acids.
-
Proteins: In some processes, proteins derived from plants or animals may be hydrolyzed to release amino acids.
-
Chemical Reagents: Chemical synthesis techniques for amino acid production involve reagents such as acylating agents, acids, and bases.
Production Process
The production of amino acids involves a combination of fermentation, chemical synthesis, and enzymatic processes. The choice of process depends on the type of amino acid being produced, the desired purity, and the scale of the operation. Below is an outline of the common methods used in amino acid manufacturing:
1. Fermentation Process
Fermentation is the most common method for producing amino acids, especially for those with significant demand, such as glutamic acid, lysine, and threonine.
- Microbial Strains: Specific strains of bacteria or fungi are used in fermentation. The microorganisms are cultured in large bioreactors, where they feed on sugars or starches and convert them into amino acids.
- Medium Preparation: A nutrient-rich medium, typically composed of sugars, salts, and nitrogen sources, is prepared to support the growth of the microorganisms.
- Fermentation: The fermentation process is carried out under controlled conditions, including temperature, pH, and oxygen levels, to maximise amino acid production.
- Extraction and Purification: Once the fermentation process is complete, the amino acids are extracted from the fermentation broth. This is typically done using filtration, centrifugation, and crystallisation methods to purify the amino acids.
2. Chemical Synthesis
Some amino acids, especially those that are less commonly produced through fermentation, can be synthesized through chemical reactions.
- Starting Materials: The chemical synthesis of amino acids typically begins with simpler organic compounds, such as ammonia or acetic acid.
- Chemical Reactions: Chemical processes like reductive amination or cyclization reactions are used to form amino acids. For example, the chemical synthesis of phenylalanine and tryptophan involves complex organic reactions.
- Purification: After the chemical synthesis, the amino acids undergo purification steps like filtration, crystallisation, and drying to ensure purity.
3. Enzymatic Processes
Enzymatic production is a more environmentally friendly and sustainable method for producing amino acids, especially in specific applications.
- Proteolytic Enzymes: These enzymes break down proteins into their constituent amino acids. Proteins are typically derived from plant sources such as soybean or corn.
- Selective Enzyme Action: Enzymes can be engineered to selectively target specific amino acids in proteins, offering a more sustainable alternative to chemical processes.
4. Extraction from Natural Sources
Certain amino acids, especially those used in niche products like gelatin, are extracted directly from natural sources.
- Animal Collagen: Collagen, found in the connective tissues of animals, is hydrolyzed to release amino acids such as glycine and proline.
Equipment for Amino Acid Manufacturing Plant
To establish a successful amino acid manufacturing plant, the following equipment is required:
- Fermenters/Bioreactors: Large vessels for cultivating microorganisms in controlled environments to produce amino acids via fermentation.
- Sterilisation Units: To ensure that the fermentation medium is free from contaminants before introducing microbial cultures.
- Filtration Systems: To separate biomass, impurities, and other solids from the fermentation broth.
- Centrifuges: Used to separate solids from liquids during fermentation.
- Drying Systems: To dry the amino acids after extraction, using methods like spray drying or freeze drying.
- Crystallisation Units: For purifying amino acids by converting them into crystals.
- Packaging Units: Automated packing systems for packaging the final amino acid product in bulk or in consumer-ready formats.
Market Trends and Demand for Amino Acids
The global demand for amino acids has been rising due to several factors, including the increased focus on health and wellness, sustainable agriculture, and the need for quality animal feed. Key market drivers include:
- Health & Nutrition: Amino acids are increasingly being used in dietary supplements, protein powders, and functional foods to promote muscle growth, weight loss, and general health.
- Animal Feed: The demand for high-quality, fortified animal feed continues to grow, as amino acids are essential for livestock health, growth, and productivity.
- Sustainability: There is a growing emphasis on plant-based and sustainable sources of amino acids, particularly in the food industry.
- Agriculture: Amino acids are gaining popularity in crop production, as they help enhance plant resilience and promote better growth.
Emerging markets, especially in Asia-Pacific, are expected to see significant growth due to expanding industrial activities and rising demand for amino acids in food and agriculture.
Financial Considerations
Establishing an amino acid manufacturing plant involves substantial investment in infrastructure, equipment, and raw materials. The key financial aspects to consider include:
- Initial Capital Investment: Significant capital is required for acquiring land, plant construction, purchasing machinery, and installing fermentation systems.
- Operational Costs: Ongoing expenses include raw material procurement, energy consumption, labor, maintenance, and quality control.
- Revenue Generation: The main revenue streams come from the sale of amino acids in various forms (powders, liquid, or crystals) to industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, animal feed, and agriculture.
- Profit Margins: Amino acids, especially high-value ones like lysine and methionine, offer attractive profit margins due to their essential roles in various industries.
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Amino acid manufacturing plants must adhere to local environmental regulations, particularly concerning waste management and water usage.
- Wastewater Treatment: Fermentation processes often produce large volumes of wastewater, requiring effective treatment systems.
- Emission Control: Emissions from fermentation and chemical processes must be managed to avoid air pollution.
- Regulatory Compliance: Depending on the region, amino acid manufacturers may need to meet various health, safety, and environmental standards.
FAQ
1. What are amino acids used for?
Amino acids are used in food, pharmaceuticals, animal feed, cosmetics, and agriculture. They play a key role in protein synthesis, health improvement, and plant growth.
2. How are amino acids produced?
Amino acids are primarily produced via fermentation, chemical synthesis, or enzymatic processes. Fermentation is the most common method for large-scale production.
3. What raw materials are needed for amino acid production?
Key raw materials include sugars, microorganisms, enzymes, and proteins. The type of raw material depends on the production method.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au

 lewisfernandas
lewisfernandas